Introduction to Morocco and Explore Morocco’s Historic Dynastic Legacy
Overview of Morocco
Morocco, officially known as the Kingdom of Morocco, is situated in the Maghreb region of North Africa, bordered by the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea. Its unique geographic position serves as a cultural bridge between Africa and Europe. Renowned for its rich history, diverse culture, and vibrant traditions, Morocco has been a focal point for travelers and scholars for centuries.

Significance in the Modern World
Morocco is strategically positioned as a link between Africa and Europe, with growing influence in global economics, tourism, and geopolitics. Its stable political environment, rich cultural heritage, and geographic location make it a key player in international relations, particularly in the Mediterranean and the Arab world.
History of Morocco
Ancient and Pre-Islamic History
Morocco’s history stretches back to prehistoric times, with human presence traced to around 90,000 BC. Long before the Phoenicians built trading posts along the coast in the 12th century BC, the area was home to Berber tribes. The region was greatly impacted by the Carthaginian and later Roman influences, especially in trade and infrastructure.
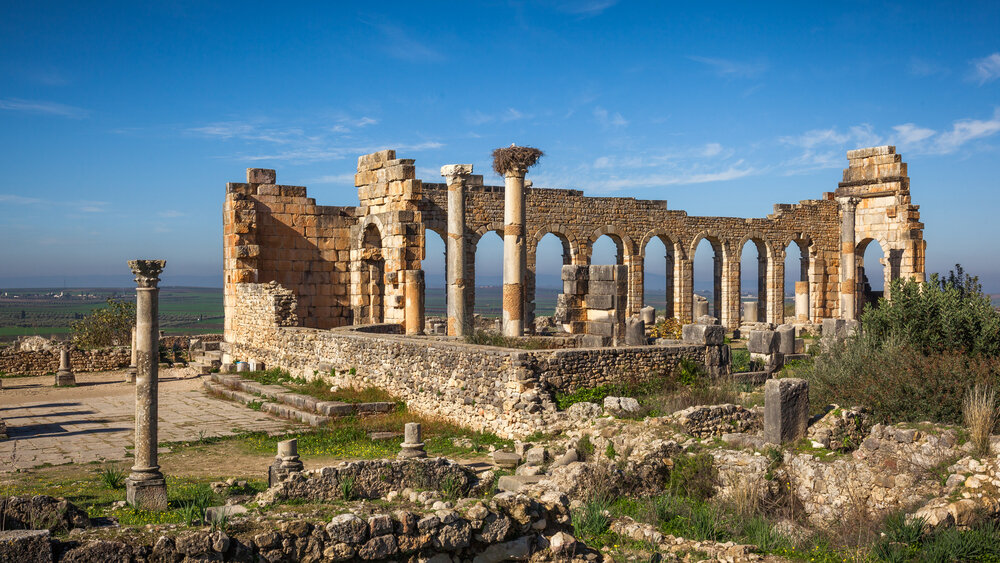

The Arrival of Islam and the Formation of the Moroccan State
The 7th century AD marked a turning point in Moroccan history with the arrival of Islam, integrating the region into the Umayyad Caliphate. By the 8th century, the Idrisid dynasty established the first Moroccan state, laying the foundation for a unique identity that blended Berber, Arab, and Islamic traditions.
The Rise of Moroccan Dynasties
Morocco’s history features the rise and fall of several powerful dynasties, such as the Almoravids and Almohads, who ruled from the 11th to 13th centuries and expanded Moroccan influence into North Africa and Spain. The Marinid and Saadian dynasties continued this legacy, with the latter achieving a notable victory over the Portuguese at the Battle of Ksar El Kebir in 1578.
Colonial Era and Struggle for Independence
During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Morocco faced increasing European colonization pressure. In 1912, France and Spain established protectorates over most of Morocco. The independence movement gained momentum in the early 20th century, culminating in the nation’s independence in 1956 under King Mohammed V, who became a symbol of unity and resistance. Place more read :Boost Mobile 2024
Geography, Map, and Flag of Morocco
Geographic Features and Map
Morocco’s diverse geography includes coastal plains, mountain ranges and expansive deserts. The Atlas Mountains run through the country’s center, separating the coastal plains from the Sahara Desert, while the Rif Mountains in the north divide the Mediterranean coast from the interior. Key cities such as Casablanca, Marrakesh, and Fes are in fertile plains, with the Sahara dominating the southeastern landscape.
The Moroccan Flag
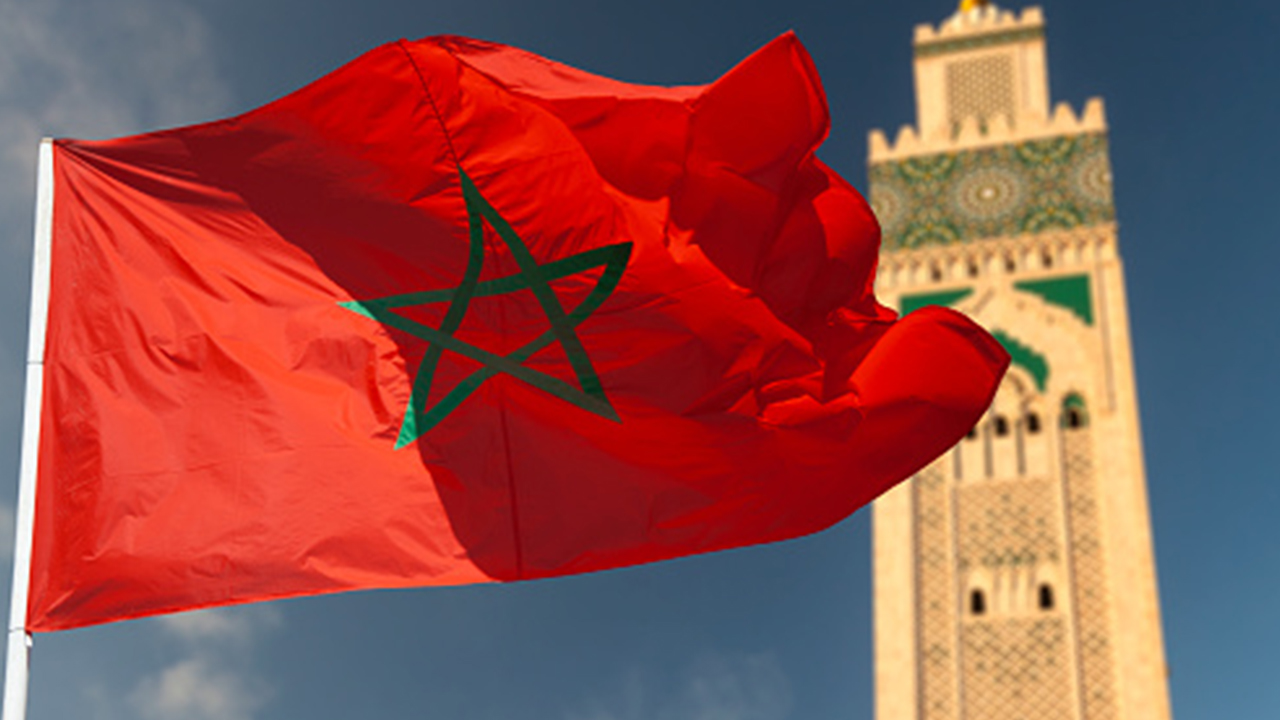
The Moroccan flag features a red background with a green five-pointed star at the center. The red represents bravery, strength, and courage, while the green star symbolizes peace, hope, and love. This flag design was adopted in 1915 during the reign of Sultan Moulay Yusef.
Capital and Major Cities
Rabat, Morocco’s capital, serves as the political and administrative hub, while Casablanca, the largest city, is the economic center known for its port and modern architecture. Other major cities include Marrakesh, famous for its historical medinas and palaces, and Fes, considered the cultural and spiritual capital.
People, Culture, and Traditions
Demographics and Ethnic Composition
Morocco’s population exceeds 37 million, composed primarily of Arab and Berber (Amazigh) ethnicities. The Berbers, the indigenous people of Morocco, maintain a strong cultural presence, particularly in rural and mountainous regions.

Religion and Language
Islam is the official religion, with the majority of Moroccans being Sunni Muslims. Arabic is the official language, while Berber languages are also widely spoken, especially in rural areas. French is frequently used in business, government, and education due to Morocco’s colonial past.
Moroccan Cuisine
Moroccan cuisine is celebrated for its rich flavors and use of spices. Popular dishes include tagine, couscous, and pastilles, reflecting the country’s diverse influences from Berber, Arab, Andalusian, and French culinary traditions.
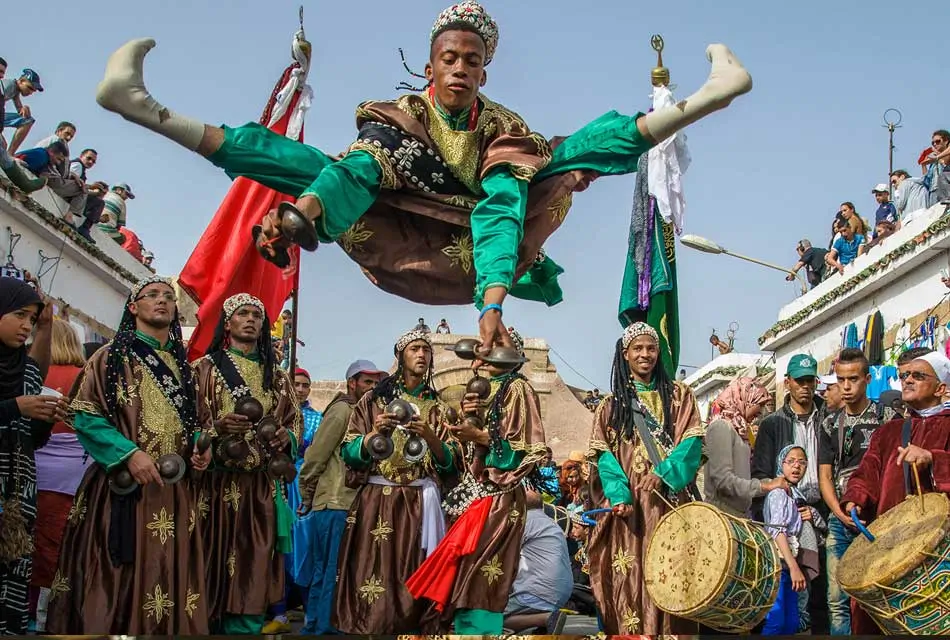
Festivals and Cultural Practices
Morocco’s cultural calendar is vibrant and filled with religious and secular festivals. Key events include Ramadan, Eid al-Fitr, Eid al-Adha, the Moussem of Moulay Idriss, the Festival of World Sacred Music in Fes, and the Marrakech International Film Festival.
Facts and Figures about Morocco
Economy and Infrastructure
Morocco has a mixed economy, with agriculture, mining, tourism, and manufacturing as key sectors. It is the world’s largest exporter of phosphates. Significant investments in infrastructure, such as high-speed rail, renewable energy, and ports, have boosted economic growth in recent years.
Political System and Governance
Morocco is a constitutional monarchy, with King Mohammed VI as the head of state. While the king retains substantial executive and legislative powers, an elected parliament and prime minister manage the government. Although progress has been made in political reforms, challenges persist in areas such as human rights.
Education and Healthcare
Education is compulsory for children aged 6 to 15, and there have been notable improvements in literacy rates and access to education. However, rural areas still face challenges. Healthcare has improved, with rising life expectancy and falling infant mortality rates, though disparities between urban and rural areas remain.
Environmental and Natural Resources
Morocco is recognized for its natural beauty and has made significant efforts in environmental conservation, particularly in water management and renewable energy. The Ouarzazate Solar Power Station is a testament to Morocco’s commitment to sustainability.
Travel to Morocco
Overview of Moroccan Tourism
Morocco attracts travelers with its diverse landscapes, rich history, and vibrant culture. From adventure enthusiasts to those seeking cultural experiences, Morocco offers something for every type of traveler.
Key Tourist Attractions
- Marrakesh: Known for its historical medinas, palaces, and the UNESCO-listed Jemaa el-Fnaa square.
- Fes: Home to one of the world’s largest car-free urban areas, Fes el-Bali, with its maze-like streets and ancient architecture.
- Sahara Desert: Offers unique experiences like camel trekking, desert camping, and exploring dunes.
- Chefchaouen: A picturesque town famous for its blue-painted streets and tranquil atmosphere.
Accommodation and Travel Tips
Morocco offers various accommodations, from luxury hotels and traditional riads to budget hostels and desert camps. Travelers should respect local customs, dress modestly, and be cautious, especially in crowded areas.
U.S. Department of State Travel Advisory
Travel Advisory Overview
The U.S. Department of State issues travel advisories for Morocco, providing information on potential risks and safety guidelines for American travelers.

Current Advisory for Morocco
As of 2024, a Level 2 travel advisory is in effect, urging travelers to exercise increased caution due to potential risks like terrorism, civil unrest, and crime in certain areas.
Safety Tips for Travelers
Travelers should stay informed, be vigilant, and take health precautions, such as drinking bottled water and avoiding street food, to prevent illness.
User Reviews and Travel Experiences
Positive Reviews and Experiences
Many travelers praise Morocco for its hospitality, diverse landscapes, and rich cultural heritage. Experiences such as desert camping and exploring medinas are often highlighted.
Challenges and Negative Reviews
Challenges include navigating crowded markets, dealing with persistent vendors, and overcoming language barriers. Safety concerns, especially for solo travelers, are also noted.
Common Themes in User Reviews
A recurring theme is the contrast between Morocco’s ancient traditions and modern developments, which fascinates many visitors.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Insights
Morocco offers a unique blend of history, culture, and natural beauty, providing a rich tapestry of experiences from its ancient cities to the Sahara Desert.
Morocco’s Global Significance
Beyond tourism, Morocco serves as a crucial gateway between Africa and Europe and is a leader in renewable energy and cultural preservation.
Final Thoughts
Morocco is a destination that captivates with its deep history, vibrant culture, and promising future, leaving a lasting impression on all who visit.



