What is an ERP system?
An ERP system stands for Enterprise Resource Planning system. It’s a software program designed to integrate and manage various core business functions within a company.
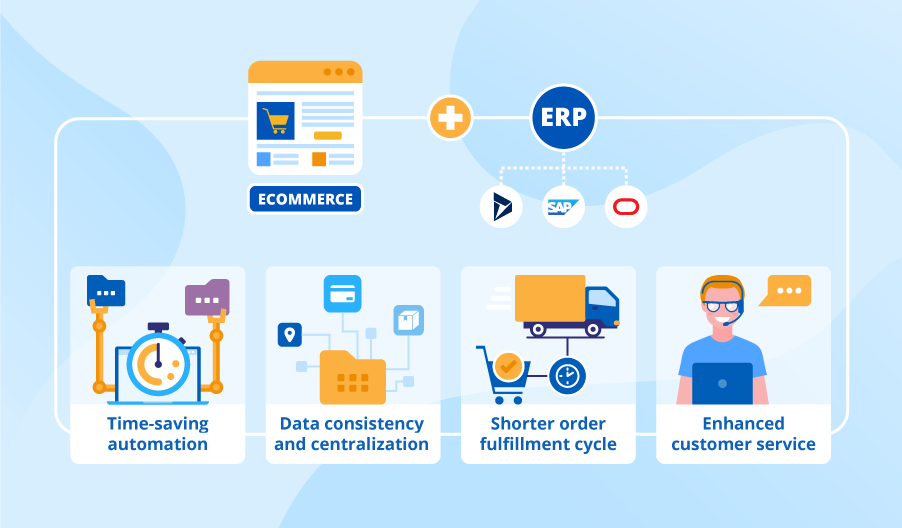
Here’s a breakdown of what an ERP system does:
- Integration: An ERP system acts as a central hub, connecting different departments and their processes. This eliminates the need for separate software programs for each function, creating a more streamlined and efficient operation.
- Core Business Functions: ERP systems typically manage a variety of functions critical to a business, including:
- Inventory Management: Tracking stock levels, generating purchase orders, and managing low-stock alerts.
- Order Processing: Streamlining the process of receiving orders, fulfilling them, and shipping them efficiently.
- Financial Accounting: Managing financial transactions, generating invoices, handling payments, and creating financial reports.
- Human Resources: Managing payroll, employee benefits, and other HR-related tasks. (This is not always included in all ERP systems)
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Storing and managing customer data, tracking interactions, and facilitating communication. (This is not always included in all ERP systems)
- Read More: Drawing:cul23ybyzfm=Basketball Dramatic and Action-Oriented
Benefits of Using an ERP System:
There are several advantages to using an ERP system, especially for businesses that are growing or managing complex operations. Here are some key benefits:
- Simplified Operations: Automating repetitive tasks and minimizing data entry errors saves time and resources.
- Improved Data Accuracy: Having a single source of truth for data across different departments eliminates data silos and ensures consistency.
- Enhanced Visibility: ERP systems provide real-time insights into various aspects of the business, allowing for better decision-making.
- Increased Efficiency: Streamlined workflows and automation lead to faster processing times and improved overall efficiency.
- Better Customer Service: Improved order processing and access to customer data can translate to better customer service experiences.
ERP Systems and E-commerce:
For e-commerce businesses specifically, ERP systems offer additional benefits:
- Inventory Management: Real-time stock visibility across multiple sales channels helps prevent stockouts and overstocking.
- Order Processing: Streamlined workflows ensure efficient order processing and faster delivery times.
- Customer Experience: Features like order tracking and personalized recommendations can enhance the customer experience.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Insights from the ERP system can inform marketing strategies, product development, and pricing decisions.
Functional Logic in ERP for E-commerce:
Functional logic refers to the set of rules and processes that define how different modules within an ERP system interact and perform specific tasks related to e-commerce operations. Here are some key areas where functional logic plays a crucial role:
- Inventory Management: Logic dictates how stock levels are tracked, purchase orders are generated based on sales and stock levels, low-stock alerts are triggered, etc.
- Order Processing: The system should process orders efficiently. Logic defines how orders are received from the e-commerce platform, validated, fulfilled through picking and packing processes, and shipped.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Functional logic governs how customer data is stored and managed, tracks order history, facilitates communication with customers, etc.
- Financial Accounting: Logic manages financial transactions related to e-commerce sales, including order payments, refunds, tax calculations, etc.
Managing Functional Logic:
Here are some general strategies for managing functional logic within an ERP for e-commerce:
- Clearly Defined Workflows: Documenting clear workflows for each process helps ensure consistency and minimizes errors.
- Conditional Logic: Implement rules to automate decision-making based on specific conditions. For example, automatically triggering shipping based on order status or calculating different shipping rates based on location.
- Customization: Many ERPs offer customization options to tailor the functional logic to specific business needs. This can involve configuring workflows, adding custom fields for data collection, or integrating with other business tools.
- Regular Reviews and Updates: As business needs and e-commerce platforms evolve, it’s crucial to regularly review and update the functional logic within the ERP system.
Additional Resources:
Since I cannot access the specific blog content, here are some resources that might be helpful:
- ERP for E-commerce Platforms: https://support.sana-commerce.com/Content/ERP-User-Guide/Ecommerce-Built-for-Your-ERP-System.htm This website discusses how ERP systems can benefit e-commerce businesses and offers some insights into integration.
- ERP Implementation and Customization: Many ERP vendors offer resources on their websites about implementing and customizing their systems for specific needs.
Understanding ERP in E-commerce
From the context we’ve gathered about Kristenly’s blog post and our previous discussions, here’s a breakdown of understanding ERP in E-commerce:
ERP Defined:
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are software programs designed to integrate and manage various business functions within a company. In the context of e-commerce, these functions can include:
- Inventory Management: Tracking stock levels, generating purchase orders, managing low-stock alerts, and ensuring accurate product availability.
- Order Processing: Streamlining the process of receiving orders, validating them, fulfilling them through picking and packing, and shipping them efficiently.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Storing and managing customer data, tracking order history, facilitating communication with customers, and personalizing their experiences.
- Financial Accounting: Managing financial transactions related to e-commerce sales such as order payments, refunds, tax calculations, and generating financial reports.
Benefits of ERP in E-commerce:
By integrating an ERP system with an e-commerce platform, businesses can enjoy several advantages:
- Simplified Operations: Automating repetitive tasks and minimizing data entry errors save time and resources.
- Improved Inventory Management: Real-time visibility into inventory levels helps prevent stockouts and overstocking, leading to better customer satisfaction and reduced costs.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Streamlined order processing and improved communication through features like order tracking and personalized recommendations can lead to happier and more loyal customers.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: ERPs provide valuable insights into sales trends, customer behavior, and operational performance, enabling businesses to make informed decisions for future growth.
Future-Proofing with Innovation:
As discussed earlier, Kristenly’s blog post likely focuses on how e-commerce businesses can leverage innovative features offered by modern ERP systems to “future-proof” their operations. These innovations might include:
- AI and Machine Learning (AI/ML): Advanced ERPs can utilize AI and ML for demand forecasting, dynamic pricing, and personalized recommendations.
- Enhanced Integrations: Modern ERPs seamlessly connect with various e-commerce platforms, marketplaces, and other business tools like CRM and marketing automation software.
- Data Analytics and Business Intelligence: Robust data analysis and business intelligence tools within ERPs allow for in-depth insights to optimize business strategies.
- Scalability and Cloud-Based Solutions: Cloud-based ERPs offer flexibility and scalability to accommodate business growth without infrastructure limitations.
The Core Argument:
Kristenly’s blog post likely argues that by embracing innovative features in Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, e-commerce businesses can “future-proof” their operations. This means adapting their strategies and processes to remain successful in the ever-changing digital landscape.
Key Innovations Discussed (Possible Content):
- Leveraging AI and Machine Learning: The post might discuss how ERP systems with AI/ML capabilities can offer functionalities like:
- Demand forecasting: Predicting future product demand based on historical data and market trends. This allows for optimized inventory management and avoids stockouts.
- Dynamic pricing: Automatically adjusting product prices based on real-time factors like competitor pricing, market shifts, and customer behavior.
- Personalized recommendations: Offering product suggestions tailored to each customer’s purchase history and browsing behavior, leading to increased sales and customer satisfaction.
- Enhanced Integrations: The blog post might explore how modern ERPs seamlessly integrate with various platforms:
- E-commerce platforms: Streamlining order processing, product management, and customer data flow between the e-commerce platform and the ERP.
- Marketplaces: Simplifying listing management, inventory updates, and order fulfillment across multiple online marketplaces.
- Other business tools: Integrating with CRM and marketing automation software for a unified ecosystem to manage all aspects of the business.
- Data Analytics and Business Intelligence: The post might highlight how advanced ERPs provide robust tools for:
- Data analysis: Examining customer behavior, sales trends, and operational performance to identify areas for improvement.
- Business intelligence: Gaining insights from data to make informed decisions regarding marketing strategies, product development, and resource allocation.
- Scalability and Cloud-Based Solutions: The blog post might emphasize the importance of ERP systems that are:
- Scalable: Able to grow and adapt alongside the business. Cloud-based solutions offer this flexibility to accommodate increasing sales volume and data needs without infrastructure limitations.
- Cost-effective: Cloud-based ERPs often require lower upfront costs and eliminate the need for extensive IT infrastructure on-site.
Additional Tips for Future-Proofing (Possible Content):
- Continuous Improvement: The post might advise businesses to continuously explore the latest ERP innovations and consider implementing them to optimize operations and stay competitive.
- Agility: Developing the ability to adapt business strategies and platforms to respond to changing customer needs and industry trends is crucial.
- Customer Experience Focus: The blog might suggest using ERP features to personalize the customer journey and deliver exceptional service through features like post-purchase communication and easy returns processes.
Conclusion:
Kristenly’s blog post likely concludes by emphasizing that embracing innovative ERP solutions is a key strategy for e-commerce businesses to ensure long-term success in an ever-evolving digital landscape. By leveraging these innovative features and continuously adapting, e-commerce businesses can build a future-proof foundation for sustained growth.