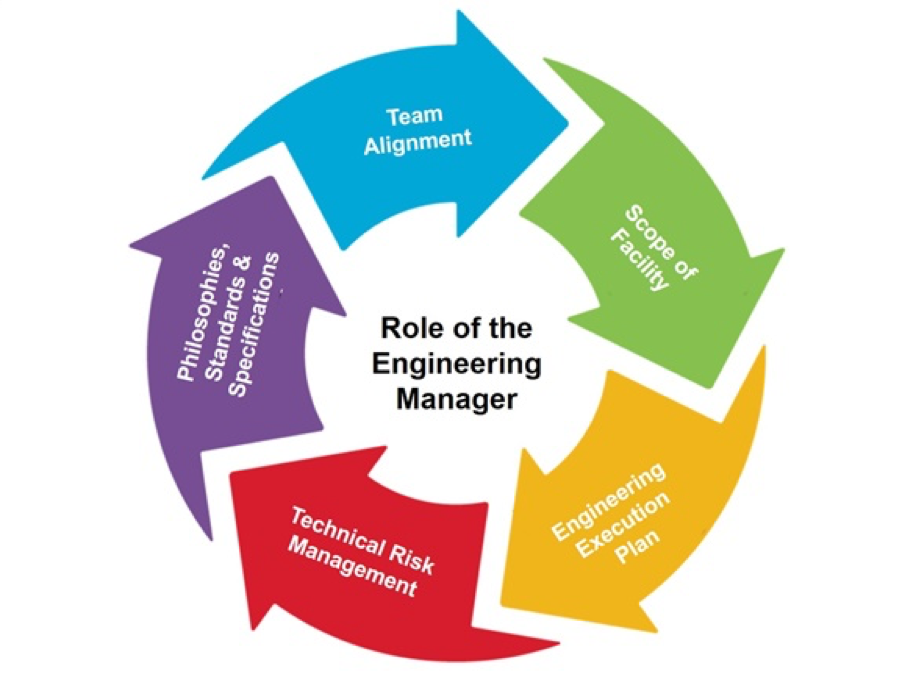
Introduction Engineering Management
Engineering control is a multi-disciplinary profession that combines technical expertise with managerial skills to lead and supervise engineering projects, and organizations.
It requires a unique blend of engineering knowledge and business acumen to ensure that projects are completed efficiently, within budget, and to the highest quality standards.

The purpose of this guide is to give you a detailed overview and understanding of engineering management and to explain and address its core concepts, key duties, and career paths.
What is Engineering Management?
masters in Engineering management is the application of engineering principles and the planning, organizing, directing, and controlling of activities that have a technical component and Improve work.
It bridges the gap between engineering and management and empowers engineers to take on leadership roles and manage projects from concept to completion.
Core Concepts in Engineering Management
1. Project Management
One of the primary responsibilities of an engineering manager is to oversee projects. This includes planning, scheduling, resource allocation, risk management, and quality control. Project management methodologies such as Agile, Waterfall, and Lean are often used by everyone to effectively solve engineering projects.
2. Operations Management
Engineering managers are responsible for ensuring that operations run smoothly and efficiently. This involves optimizing processes, improving productivity, and maintaining high standards of quality and safety.
3. Product Development:
From ideation to launch, engineering managers play a critical role in the product development process. They coordinate with various departments, manage timelines, and ensure that products meet market needs and regulatory requirements.
4. Financial Management
Budgeting, cost estimation, and financial planning are crucial aspects of engineering management. Managers must ensure that projects are financially viable and resources are used effectively.
5. Human Resource Management
Leading engineering teams requires effective communication, motivation, and conflict resolution skills. Engineering managers must recruit, train, and develop talent while fostering a positive work environment.
7. Strategic Planning
Long-term planning and strategic decision-making are essential for the success of engineering projects and organizations. Managers must align engineering goals with business objectives and anticipate future trends and challenges.
Key Responsibilities of an Engineering Manager
Leadership and Team Management: Engineering managers lead teams of engineers, providing direction, support, and motivation. They are responsible for setting goals, assigning tasks, and ensuring that team members have the resources they need to succeed.
1. Project Planning and Execution
Managers create detailed project plans, define project scope, set milestones, and establish timelines. They oversee the execution of projects, monitor progress, and make adjustments as needed to stay on track.
2. Resource Allocation
Efficient use of resources is critical in engineering projects. Managers allocate resources such as personnel, equipment, and materials, ensuring that they are used effectively and efficiently.
3. Risk Management
Identifying, assessing, and mitigating risks is a key responsibility. Engineering managers develop risk management plans and implement strategies to minimize potential impacts on the project.
4. Quality Assurance
Maintaining high standards of quality is essential in engineering. Managers implement quality control processes, conduct inspections, and ensure that all work meets or exceeds industry standards and specifications.
5. Communication and Collaboration
Effective communication is vital for the success of engineering projects. Managers facilitate communication between team members, departments, and stakeholders, ensuring that everyone is informed and aligned.
6. Budgeting and Financial Oversight
Engineering managers are responsible for managing project budgets, tracking expenses, and ensuring that projects stay within financial constraints. They also identify cost-saving opportunities and optimize resource use.
Essential Skills for Engineering Managers
1. Technical Expertise
A strong background in engineering is essential. Managers must have a deep understanding of engineering principles, practices, and technologies relevant to their field.
2. Leadership and Management Skills
Effective leadership involves inspiring and motivating teams, making strategic decisions, and managing conflicts. Strong management skills are necessary for organizing and overseeing projects and operations.
3. Communication Skills
Clear and concise communication is crucial for conveying information, instructions, and feedback. Managers must be able to communicate effectively with team members, stakeholders, and clients.
4. Problem-Solving and Analytical Skills
Engineering managers must be adept at identifying problems, analyzing data, and developing innovative solutions. Critical thinking and analytical skills are essential for making informed decisions.
5. Project Management Skills
Proficiency in project management methodologies and tools is important for planning, executing, and monitoring projects. Knowledge of software like Microsoft Project, Asana, or Trello can be beneficial.
6. Financial Acumen
Understanding financial principles, budgeting, and cost management is essential for overseeing project finances and ensuring profitability.
7. Interpersonal Skills
Building and maintaining positive relationships with team members, clients, and stakeholders is important for fostering collaboration and achieving project goals.
8. Time Management
Effective time management is crucial for meeting deadlines and ensuring that projects stay on schedule.
1. Entry-Level Positions
Starting positions may include roles such as project engineer, assistant project manager, or team lead. These roles provide opportunities to gain experience and develop management skills.
2. Mid-Level Positions
With experience, engineers can advance to positions such as project manager, operations manager, or engineering manager. These roles involve greater responsibility for managing projects, teams, and budgets.
3. Senior-Level Positions
Senior positions include roles such as director of engineering, vice president of engineering, or chief technology officer (CTO). These roles involve strategic planning, executive decision-making, and overseeing large teams and complex projects.
4. Specialized Roles
Some engineering managers may choose to specialize in areas such as quality assurance, research and development, or supply chain management. Specialized roles allow managers to focus on specific aspects of engineering management.
1. Educational Background
A bachelor’s degree in engineering is typically required for entry-level positions. Many engineering managers also hold a master’s degree in engineering management (MEM) or a Master of Business Administration (MBA) with a focus on technology management.
2. Certifications
Professional certifications can enhance career prospects and demonstrate expertise. Relevant certifications include Project Management Professional (PMP), Certified Scrum Master (CSM), and Six Sigma Green Belt.
3. Continuing Education
Staying current with industry trends, emerging technologies, and best practices is important. Many engineering managers pursue continuing education through workshops, conferences, and online courses.

Challenges in Engineering Management
1. Balancing Technical and Managerial Responsibilities
Engineering managers must balance their technical expertise with managerial duties. This can be challenging, as both aspects require different skills and approaches.
2. Managing Complex Projects
Engineering projects often involve complex technical challenges, tight deadlines, and limited budgets. Managers must navigate these complexities while ensuring project success.
3. Adapting to Technological Changes
Rapid advancements in technology require engineering managers to stay updated and continuously adapt to new tools, techniques, and innovations.
4. Handling Conflicts and Issues
Managing a diverse team can lead to conflicts and issues that need to be resolved effectively. Engineering managers must have strong interpersonal and conflict-resolution skills.
5. Ensuring Quality and Compliance
Maintaining high standards of quality and ensuring compliance with industry regulations and standards is a critical responsibility. Managers must implement robust quality control processes and stay informed about regulatory requirements.
reselt
Engineering management is a dynamic and rewarding field that combines technical expertise with management skills to lead engineering projects and teams to success. By mastering the core concepts, key responsibilities, and essential skills outlined in this guide, aspiring engineering managers can build a strong foundation for a successful career.
Continuous learning, professional development, and adaptability are key to thriving in this ever-evolving discipline. Whether you are just starting your career or looking to advance to higher levels of leadership, engineering management offers a wide range of opportunities for growth and achievement.