Your heart rate, the number of times your heart beats per minute, is a vital indicator of your overall health and well-being. While some changes are natural, persistently high or low heart rates can signal underlying health problems.
Fortunately, there are several strategies you can employ to gain more control over your heart rate, enabling better cardiovascular health and a sense of calm.

A Personalized Approach
Before diving into control methods, it’s crucial to understand your target heart rate zone. This range, expressed in beats per minute (bpm), represents the optimal heart rate while running for cardiovascular exercise. It varies based on your age and fitness level. A simple online calculator or consultation with a healthcare professional can help you determine your target zone.
Causes of an Increased Heart Rate:
Physical Activity:
Exercise naturally elevates your heart rate as your body demands more oxygen. This is a healthy response, and your heart rate will gradually return to normal after you rest.
Stress:
When stressed, your body releases hormones like adrenaline, which increase heart palpitations rate and blood pressure to prepare you for a perceived threat. Chronic stress can keep your heart rate elevated over time.
Dehydration:
When you’re dehydrated, your blood volume decreases. To maintain circulation, your heart beats faster to deliver oxygen and nutrients throughout your body.
Medications:
Certain medications, including decongestants, asthma inhalers, and some thyroid medications, can raise your heart rate as a side effect.
Medical Conditions:
Underlying health issues like anemia, thyroid problems, heart disease, and infections can also contribute to a rapid heart rate.
Tips to Control Your Heart Rate:
Manage Stress:
Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga to combat stress and its impact on your heart rate.
Stay Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day to maintain proper blood volume and prevent dehydration-induced heart rate spikes.
Healthy Diet:
Choose a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit processed foods, saturated fats, and added sugars, which can contribute to heart health issues that affect heart rate
Exercise Regularly:
Regular physical activity strengthens your heart muscle, making it more efficient and requiring fewer beats per minute to pump blood effectively.
Reduce Stimulants:
Limit your intake of caffeine and nicotine, as these stimulants can temporarily increase your heart rate.
Deep Breathing Exercises:
When you feel your heart racing, try deep breathing. Inhale slowly through your nose for a count of four, hold for seven, and exhale slowly through pursed lips for eight. Repeat this cycle several times to calm yourself and lower your heart rate.
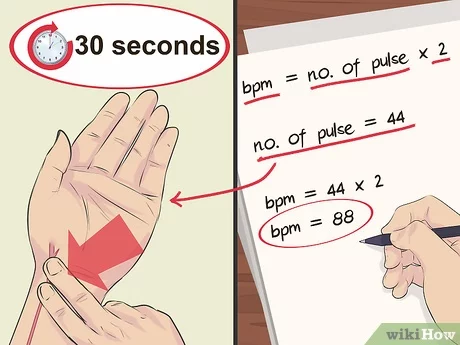
Lifestyle Modifications for Long-Term Control
Several lifestyle changes can significantly impact your heart rate over time. Here are some key areas to focus on:
Embrace Exercise:
Regular physical activity strengthens your heart muscle, making it more efficient at pumping blood. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise per week.
Manage Stress:
Chronic stress triggers the release of hormones like adrenaline, which can elevate your heart rate. Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, or yoga to manage stress effectively.
Maintain a Healthy Weight:
Excess weight puts a strain on your heart. Losing weight, even a moderate amount, can improve your heart rate and overall cardiovascular health.
Fuel Your Body Right:
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains provides your body with the nutrients it needs to function optimally. Limit processed foods, saturated fats, and added sugars, which can contribute to heart health issues.
Stay Hydrated:
Dehydration can increase your heart rate as your heart works harder to circulate blood. Drink plenty of water throughout the day to stay adequately hydrated.
Limit Stimulants:
Caffeine and nicotine are stimulants that can temporarily increase your heart rate. Consider reducing your intake of coffee, tea, and other caffeinated beverages, as well as avoiding smoking altogether.


